Pipe Three Layer Polyethylene Coating Specification

Creating a comprehensive guide on the three-layer polyethylene coating specification for pipes, including coating procedure and qualification, qualification of the applied coating, and inspection and testing, involves a detailed exploration of each aspect. This guide will cover the essential elements of each section, ensuring a thorough understanding of the process and standards involved.
Introduction to Three-Layer Polyethylene Coating
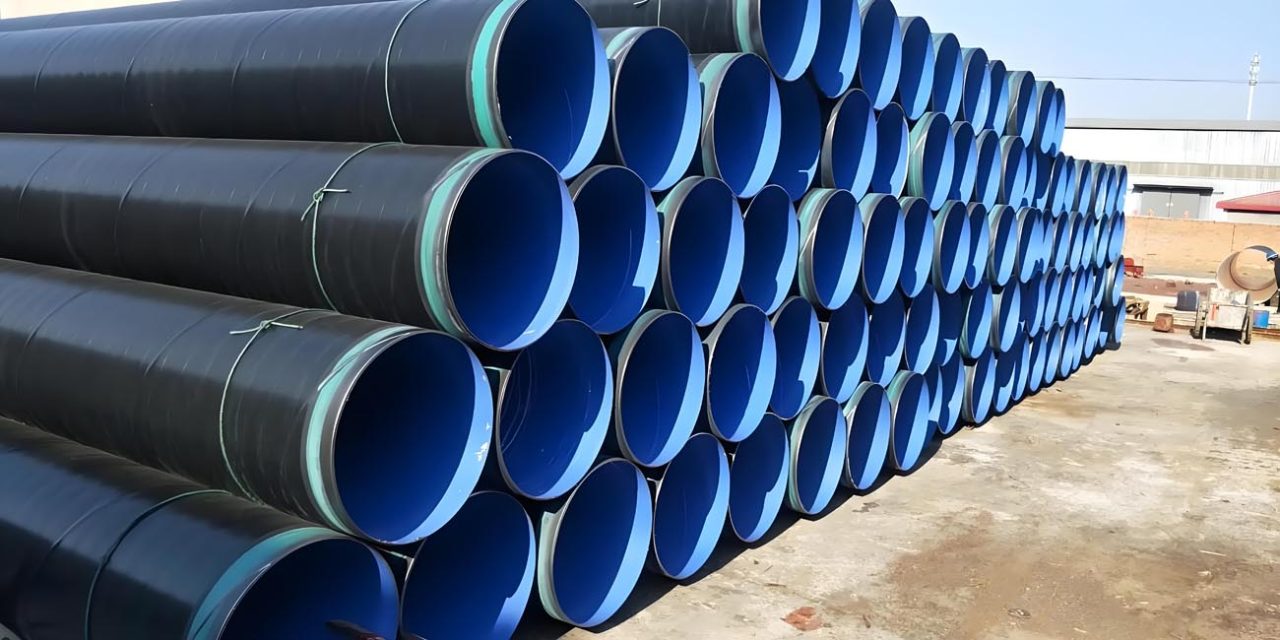
Three-layer polyethylene (3LPE) coating is a robust protective system used to safeguard steel pipes – 3LPE Coating Anti-Corrosion SSAW Steel Pipe against corrosion. This coating system combines the properties of fusion-bonded epoxy, adhesive, and polyethylene to provide superior protection against moisture, chemicals, and mechanical damage. The 3LPE system is widely used in the oil and gas industry, water pipelines, and other applications where long-term durability and corrosion resistance are critical.
1. Coating Procedure and Qualification
Coating Procedure
The 3LPE coating process involves several key steps, each crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and durability of the coating. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the procedure:
- Surface Preparation:
- Cleaning: The pipe surface must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any rust, mill scale, or contaminants. This is typically achieved through abrasive blasting, which creates a rough surface profile that enhances coating adhesion.
- Pre-Heating: The pipe is pre-heated to a specific temperature to ensure optimal adhesion of the epoxy layer.
- Application of Fusion-Bonded Epoxy (FBE):
- Epoxy Coating: The first layer of the 3LPE system is a fusion-bonded epoxy, applied as a powder to the pre-heated pipe surface. The heat causes the epoxy to melt and form a continuous, uniform layer that provides excellent adhesion and corrosion resistance.
- Application of Adhesive Layer:
- Adhesive Coating: A copolymer adhesive is applied over the epoxy layer. This adhesive serves as a bonding agent between the epoxy and the polyethylene layer, ensuring a strong, cohesive coating system.
- Application of Polyethylene Layer:
- Polyethylene Coating: The final layer is a polyethylene coating, extruded onto the adhesive layer. This layer provides mechanical protection and additional resistance to environmental factors.
- Cooling and Curing:
- Cooling: The coated pipe is allowed to cool, solidifying the polyethylene layer and ensuring the integrity of the entire coating system.
Qualification of Coating Procedure
The qualification of the coating procedure involves verifying that each step of the process meets industry standards and specifications. This includes:
- Procedure Qualification Records (PQR): Documenting the specific parameters used during the coating process, such as temperatures, application speeds, and material specifications.
- Operator Qualification: Ensuring that personnel involved in the coating process are adequately trained and qualified to perform their tasks.
2. Qualification of Applied Coating
The qualification of the applied coating ensures that the 3LPE system meets the required performance standards and specifications. This involves a series of tests and inspections to verify the coating’s integrity and effectiveness.
Testing and Evaluation
- Adhesion Testing:
- Peel Test: This test evaluates the adhesion strength between the layers of the coating system – What are the advantages of using a double-layer FBE coating system compared to a single-layer coating?. A sample of the coating is peeled from the pipe surface, and the force required to remove it is measured.
- Impact Resistance:
- Impact Test: The coating is subjected to impact forces to assess its ability to withstand mechanical damage. This test ensures that the coating can protect the pipe during handling and installation.
- Cathodic Disbondment Test:
- Disbondment Evaluation: This test measures the coating’s resistance to cathodic disbondment, a common form of coating failure in buried pipelines. The test involves applying an electrical current to the coated pipe and evaluating the extent of disbondment over time.
- Thermal Aging:
- Aging Test: The coating is exposed to elevated temperatures for a specified period to assess its long-term thermal stability and performance.
- Chemical Resistance:
- Chemical Exposure Test: The coating is exposed to various chemicals to evaluate its resistance to chemical attack and degradation.
- Thickness Measurement:
- Coating Thickness: The thickness of each layer of the 3LPE system is measured to ensure compliance with specified standards.
3. Inspection and Testing
Inspection and testing are critical components of the 3LPE coating process, ensuring that the applied coating meets all required specifications and standards.
Inspection Procedures
- Visual Inspection:
- Surface Examination: Inspectors visually examine the coated pipe for any defects, such as pinholes, blisters, or uneven coverage.
- Holiday Detection:
- Holiday Test: A high-voltage holiday detector is used to identify any discontinuities or defects in the coating that could lead to corrosion.
- Dimensional Inspection:
- Pipe Dimensions: The dimensions of the coated pipe, including diameter and wall thickness, are measured to ensure compliance with design specifications.
- Adhesion and Bonding:
- Adhesion Verification: Inspectors verify the adhesion between the coating layers and the pipe surface, ensuring a strong bond.
Testing Standards
The inspection and testing of 3LPE coatings are conducted in accordance with industry standards, such as those set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards provide guidelines for testing methods, acceptance criteria, and documentation requirements.